Regulatory change management is a constant reality for fintech companies. Rules can shift quickly, and sometimes regulators apply old requirements to new products. For founders, legal teams, and compliance officers, staying on top of these changes is now a key part of running the business.
This guide walks through the essentials of regulatory change management. You’ll learn how to track new rules, evaluate their impact, adjust your policies, and keep your teams prepared. We’ll also look at the main regulators fintechs need to follow, common challenges that get in the way, and approaches that help turn compliance into an advantage.
What Is Regulatory Change Management?
Regulatory change management is the process companies use to spot, understand, and respond to new or updated laws and rules. For fintechs, this is especially important because products often touch many areas at once, like banking, securities, payments, and state licensing. A single change in one rule can affect everything from product design to customer onboarding to reporting.
At its heart, regulatory change management comes down to three steps: keeping track of new rules, figuring out how they apply to your business, and making the right changes inside your company. That might mean updating policies, adjusting systems, or training your team on what’s new. It also means documenting decisions and making sure responsibilities are clear, so regulators and partners can see how compliance is being handled.
Its purpose goes beyond just staying compliant. The real value is creating a repeatable process that helps your company adapt without losing momentum. For fintech leaders, this turns regulatory updates from a constant source of stress into something that can be handled with structure and confidence.
Core Components Of Regulatory Change Management
Regulatory change management becomes easier when broken into clear steps. Instead of reacting to every update, fintech companies can use a framework that covers monitoring, assessment, communication, and follow-through. Each part of the process helps teams respond quickly and with focus.
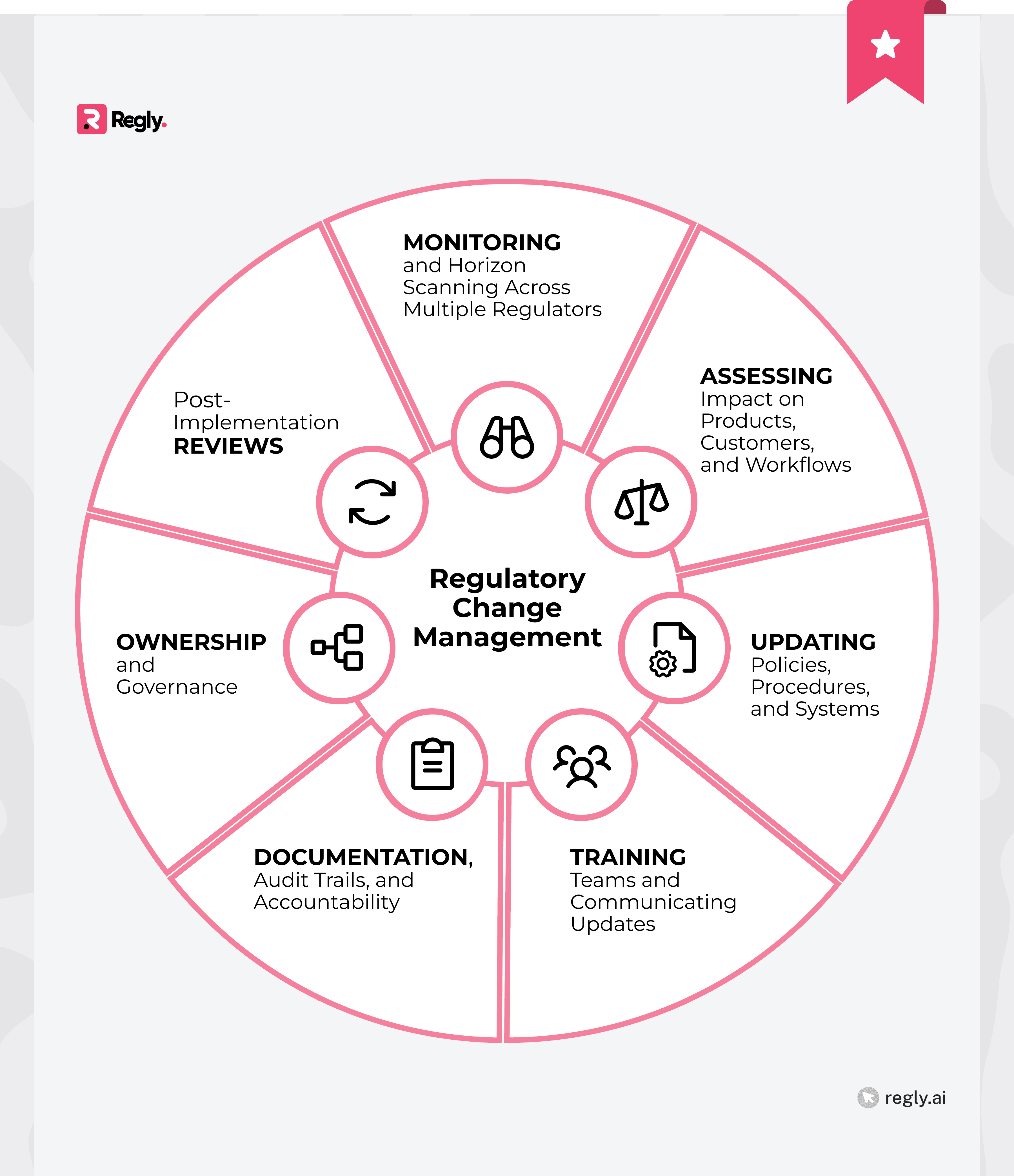
1. Monitoring And Horizon Scanning Across Multiple Regulators
The foundation of regulatory change management is knowing what rules are coming down the pipeline. For fintechs, this means tracking updates not just from federal regulators, but also from state agencies and, in many cases, international authorities. Missing even one development can create risks that spread across products, customers, and partnerships.
This kind of monitoring, often called horizon scanning, goes beyond passively watching news feeds. It’s about building structured ways to capture updates, filter them for relevance, and share them with the right people. Many fintechs use a mix of regulatory alerts, industry groups, and technology platforms like Regly to make the flow of information manageable.
What matters most is consistency. When monitoring is predictable, compliance teams can spot trends early, reduce surprises, and start planning for changes before they become urgent. This steady approach lays the foundation for everything else in regulatory change management.
2. Assessing Impact On Products, Customers, And Workflows
Once a new rule or guidance is identified, the next step is understanding what it means for your business. For fintechs, that often means looking at several layers at once: the product itself, how customers use it, and the internal processes that keep everything running.
Impact assessments make this practical. They help answer questions like: Will onboarding requirements change? Will transaction monitoring or reporting need adjustments? Do product terms or customer disclosures need updates? Each answer can uncover ripple effects that reach beyond compliance and into operations or even user experience.
A structured assessment process keeps important details from slipping through the cracks. By bringing product, legal, and operations teams into the conversation early, fintechs can spot risks sooner, adjust plans, and decide where systems or policies may need to shift.
3. Updating Policies, Procedures, And Systems
After assessing impact, the focus shifts to making concrete updates inside the organization. This is where regulatory change management moves from analysis to action. Policies may need revisions to match new requirements, and procedures often need tweaks so staff know how to handle daily tasks under the updated framework.
Technology plays a big role, too. A change in the rules might call for new transaction monitoring settings, updated onboarding steps for customers, or refreshed reporting tools. Fintechs that build compliance into their systems can adapt more quickly and keep operations running smoothly.
Documentation finally ties it all together. Recording when and why updates were made creates a clear trail that helps internal teams stay aligned and gives external partners and regulators confidence that compliance is being handled properly.
4. Training Teams And Communicating Updates
Even the best policy updates fall short if teams don’t understand them. Training and communication are essential parts of regulatory change management because they bridge the gap between written rules and daily practice.
The best training is simple and practical. A short session or a quick reference guide often works better than a long presentation. The goal is to help employees see how the changes fit into their own work, irrespective of whether they’re in customer service, product development, or operations.
Good communication also reaches beyond the company. Partners, vendors, and sometimes even customers may need to know about updates. Sharing information clearly and on time reduces confusion, strengthens trust, and shows that the firm is handling compliance with care.
5. Documentation, Audit Trails, And Accountability
Strong documentation is at the heart of regulatory change management. Every step, from spotting a new rule to updating a workflow, should leave a clear record. This keeps internal teams aligned and gives regulators, auditors, and partner banks the confidence that compliance is being handled properly.
An effective audit trail shows not only what changes were made, but also when and by whom. This level of accountability reduces confusion later and helps demonstrate that compliance steps were taken seriously.
For fintechs, building this discipline early pays off. Instead of scrambling to recreate past decisions, companies have a reliable history of how they managed regulatory change. That history becomes an asset during exams, investor reviews, or partner negotiations.
6. Ownership And Governance
Regulatory change management falls apart without clear ownership. When no one knows who's responsible for tracking and implementing updates, things get missed or misunderstood. This happens constantly in fintechs where everyone's moving fast and wearing multiple hats. The fix is straightforward: assign specific people to handle both the big-picture strategy and the day-to-day work of managing regulatory changes.
Governance is the backbone of an effective ownership system. Think of it as the operating rhythm that keeps everyone aligned. Regular touchpoints between teams, a paper trail of who approved what, and clear escalation routes when issues come up. Without these basics, compliance updates end up living in silos where the legal team knows one thing, product knows another, and operations is working off outdated information. Good governance connects these dots and keeps regulatory changes moving through the organization instead of getting stuck in someone's inbox.
7. Post-Implementation Reviews
Regulatory change management doesn’t end when updates are rolled out. A post-implementation review helps confirm whether changes are working as intended and highlights areas that need more attention. For fintechs, this step is especially useful because even small process gaps can create larger compliance risks down the line.
Reviews don’t have to be complicated. Teams can simply revisit what was updated, check whether new policies or systems are working as intended, and gather feedback from the people who use them every day. The goal is to spot practical improvements and make sure the changes fit naturally into existing workflows.
When reviews become a regular part of the process, they create a feedback loop that strengthens regulatory change management over time.
The Importance of Regulatory Change Management in Fintech
For fintech companies, regulatory change management directly affects growth, risk, and the ability to maintain strong relationships with customers and partners. A structured approach helps companies keep pace with shifting rules while continuing to innovate.
Promotes ongoing compliance with evolving laws and regulations: Financial regulations change often, and they rarely move in just one direction. Federal agencies, state regulators, and international bodies all issue updates that can affect fintech models in different ways. A consistent process for monitoring and adapting to these shifts allows companies to keep pace without losing focus on their core business.
Prevents costly fines, penalties, and enforcement actions: Regulatory enforcement has become more active, especially in areas like consumer lending, crypto, and payments. When companies miss or misinterpret a change, the result can be fines, legal settlements, or public enforcement actions. These outcomes are not only expensive and time-consuming, but they also distract leadership from building the business. A proactive approach to change management mitigates that risk.
Protects critical banking and investor relationships: Sponsor banks, payment partners, and investors increasingly want proof that fintechs can handle regulatory expectations. A clear process for managing change shows maturity and reliability. This can make the difference between winning a new partnership and being passed over for another firm with stronger compliance practices.
Builds and maintains customer trust and confidence: Customers want confidence that their money and data are protected. When a company can adapt responsibly to regulatory changes, it signals stability and professionalism. This trust is difficult to rebuild once lost, which makes regulatory change management a direct contributor to customer loyalty and reputation.
Enables faster entry into new markets and product launches: Each new product line or market entry comes with its own set of rules. Without a structured way to evaluate and implement those rules, fintechs often face delays. With a straightforward process, teams can identify requirements early, adjust plans, and move forward more efficiently.
Provides a structured way to manage operational risk: When updates are handled informally, essential steps can fall through the cracks. That creates operational gaps that might not be obvious until regulators or partners raise concerns. A structured regulatory change framework creates consistency, reduces errors, and gives teams clarity on what needs to happen and when.
Turns compliance into a competitive advantage: Strong compliance practices can be more than defensive. They position a fintech as a reliable partner, attract institutional investors, and even accelerate partnerships with banks. Companies that manage regulatory change effectively demonstrate resilience and readiness, which can be a powerful differentiator in a crowded market.
Top Challenges Fintechs Face in Regulatory Change Management (And Their Solutions)
Regulatory change management can feel overwhelming for fintech companies. The pace of new rules, the complexity of overlapping jurisdictions, and the limited resources most startups operate with all create pressure. Recognizing the most common challenges is the first step toward solving them.
Challenge | Practical Solutions |
|---|---|
Tracking rules from multiple regulators | Centralize monitoring to cut noise and focus on relevant rules |
Ambiguity in applying old laws to new models | Document interpretations and seek expert input for clarity |
Limited compliance staff and resources | Use outsourced support or automation to extend capacity |
Partnership pressures from sponsor banks and vendors | Define responsibilities upfront and keep clear records |
Constantly changing state licensing and reporting | Maintain a licensing calendar with reminders and templates |
Information overload from fragmented updates | Consolidate updates and prioritize by impact and relevance |
Balancing compliance needs with fast product development cycles | Involve compliance early in product design to avoid rework |
1. Tracking Rules From Multiple Regulators
One of the toughest parts of regulatory change management is the sheer number of authorities fintechs must follow. A lending platform, for example, might need to track updates from the CFPB, state regulators, and sometimes even the FDIC, if partnering with banks. A payments company faces oversight from the FinCEN, CFPB, FTC, and dozens of state licensing agencies at the same time.
With so many moving parts, critical developments can easily be missed. Relying on email alerts or scattered news feeds often leads to information overload, with no clear way to separate what is relevant from what is not. That can slow down response time and create real compliance risk.
The most practical approach is to centralize monitoring with specialized tools that consolidate updates across regulators and jurisdictions. This way, instead of chasing every headline, teams can focus on the rules that matter most for their products and customers.
2. Ambiguity in Applying Old Laws to New Models
Many fintech products operate in regulatory gray areas. Laws that were written for traditional banks or brokerages often get applied to models like Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL), stablecoins, or robo-advisors. The problem is that regulators do not always spell out exactly how those legacy rules fit. This leaves fintech leaders trying to interpret requirements while still moving their business forward.
Ambiguity creates risk. For instance, companies may take a conservative approach that slows innovation, or they may push forward only to discover later that regulators view their interpretation differently. Both outcomes can be costly, either in lost opportunities or in compliance exposure.
The best way to manage this uncertainty is to build a process for structured analysis. That includes reviewing existing rules carefully, seeking outside legal or compliance expertise when needed, and documenting the reasoning behind decisions. By creating a clear record, fintechs show they acted thoughtfully, even if the rules were unclear at the time.
3. Limited Compliance Staff and Resources
Most fintechs operate with lean teams, and compliance often competes with product development, fundraising, and customer growth for both time and budget. In many cases, a small compliance team is responsible for tracking rules across multiple regulators while also managing day-to-day tasks like monitoring transactions or preparing reports.
The challenge is that regulatory change management requires consistent attention. Without enough staff, updates may be noticed late, implemented unevenly, or dropped altogether. This increases the chance of missed obligations, which can create both financial and reputational risk.
There are practical ways to manage these constraints. Some companies bring in outsourced compliance support to handle specialized work without taking on the cost of a full in-house team. Others invest in systems that automate parts of the change process and reduce manual tracking.
4. Partnership Pressures From Sponsor Banks and Vendors
For many fintechs, success depends on strong partnerships with sponsor banks, processors, and technology vendors. These partners often introduce their own compliance requirements, which may be stricter than what regulators mandate. That adds another layer of complexity on top of the already heavy regulatory workload.
The pressure comes from the fact that partners hold leverage. A bank that feels uncomfortable with a fintech’s compliance program may delay approvals, restrict products, or even end the relationship. Vendors, too, may require extra reporting or certifications to protect their own risk exposure. Meeting these demands can stretch limited compliance resources and create friction across teams.
The most effective way to manage partnership pressures is with clear communication and documentation. When responsibilities are defined upfront, it reduces duplication of work and avoids last-minute surprises. Regular check-ins with partners also help catch issues before they escalate.
Tools like Regly’s AI-powered compliance management software can support this process by centralizing requirements from multiple stakeholders in one place. Compliance teams can assign tasks, track progress, and maintain records that show how firms are meeting partner obligations.
5. Constantly Changing State Licensing and Reporting Requirements
State-level regulation is one of the most demanding areas for fintechs. Each state has its own licensing rules for money transmission, lending, and data privacy. These requirements often change with little notice, and keeping up with fifty different jurisdictions can feel like a full-time job.
The challenge is not only the volume of updates but also their variety. Some states adjust reporting deadlines, while others add new disclosure rules or modify license renewal processes. Missing even one change can delay operations or expose a company to penalties.
Fintechs that succeed here usually build a structured system for monitoring state updates. That includes maintaining a calendar of renewal deadlines, assigning ownership for specific states, and creating templates for recurring reports. By treating state compliance as an organized workflow, companies can reduce the chance of last-minute surprises.
6. Information Overload From Fragmented Regulatory Updates
Regulatory updates rarely come in one clear package. Instead, they arrive as press releases, speeches, enforcement actions, policy guidance, or even informal statements from regulators. For fintechs, this fragmented flow makes it hard to separate what is critical from what can wait. The result is information overload that slows teams down and risks important changes being overlooked.
The main challenge often lies in filtering. Not every update requires action, but without a system to sort them, compliance staff may spend hours sifting through irrelevant notices. That time could be better spent on analysis and implementation.
A practical solution is to create a structured filtering process. Updates can be tagged by relevance, grouped by regulator, and prioritized based on impact. This way, the right people see the right information at the right time.
7. Balancing Compliance Needs With Fast Product Development Cycles
Fintechs thrive on speed. New features, market launches, and customer-facing updates often move on tight timelines. At the same time, regulatory change management requires careful review, documentation, and implementation. Balancing these two is typically a great challenge for fintech leaders.
When compliance is treated as an afterthought, products may need to be redesigned late in the process. That slows launches, frustrates teams, and creates extra costs. On the other hand, prioritizing speed without compliance oversight can expose the company to unnecessary risk.
The best approach is to bring compliance into product development early. If legal and compliance staff are involved in design discussions, they can spot potential issues before they require major rework. This makes timelines more predictable and keeps compliance aligned with business goals.
Key US Regulators And Updates Fintechs Must Track
Fintech companies operate in one of the most complex regulatory environments in the financial sector. Multiple agencies oversee different parts of the business, and their priorities often shift. Understanding who the main regulators are and what areas they focus on is an essential part of effective regulatory change management.
CFPB: Consumer Financial Protection Rules
The Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) is one of the most active regulators for fintech companies. Its mandate is to protect consumers in financial services, which means its rules reach into lending, payments, credit reporting, debt collection, and emerging models like BNPL.
For fintechs, CFPB oversight often comes down to three areas: disclosures, fair treatment, and complaint handling. Rules require companies to provide clear terms, avoid practices that could be considered deceptive, and have systems for tracking and resolving customer complaints. The CFPB also looks closely at how fintechs market products, making advertising reviews an integral part of compliance programs.
One of the CFPB’s current priorities is digital lending. Recent guidance has focused on BNPL providers, credit reporting practices, and the use of artificial intelligence in underwriting. Fintechs in these spaces need to pay particular attention to new rules and policy statements, as they can shift quickly with changes in leadership and enforcement priorities.
A structured regulatory change management process helps fintechs keep pace with the CFPB’s updates. By monitoring rulemaking, enforcement trends, and public statements, companies can anticipate shifts before they become formal requirements. This proactive approach mitigates the risk of sudden disruptions and keeps customer-facing operations aligned with regulatory expectations.
SEC And FINRA: Securities, Investments, And Crypto
The SEC and FINRA oversee how securities are offered, traded, and supervised. For fintechs, this includes platforms that provide digital investment advice, broker-dealer services, equity crowdfunding, and crypto asset products that may qualify as securities.
The SEC focuses heavily on disclosures, investor protection, and conflicts of interest. Fintechs offering investment products must be clear about fees, risks, and how customer assets are handled. FINRA, as a self-regulatory body, adds another layer by requiring member firms to maintain supervisory systems, conduct due diligence on new products, and keep detailed records.
Crypto adds further complexity. The SEC has taken the position that many tokens meet the definition of securities, while FINRA has been developing guidance for member firms that want to engage with digital assets. For fintechs in this space, regulatory change management is crucial, since interpretations evolve quickly and enforcement actions often set precedents.
CFTC: Derivatives And Digital Assets
The Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) regulates futures, swaps, and other derivatives. Its role in fintech has grown as digital assets have expanded into derivatives markets. Products such as crypto futures, options, and leveraged trading platforms often fall under CFTC jurisdiction.
For fintechs, the CFTC’s oversight includes requirements for reporting, recordkeeping, customer protections, and anti-manipulation controls. This agency also pays close attention to how firms market complex products to retail investors, making clear disclosures and risk warnings a priority.
The challenge is that the line between securities and commodities is still developing in the digital asset space. Some tokens are treated as securities by the SEC, while others are viewed as commodities by the CFTC. This overlap creates uncertainty for fintechs building products in crypto trading or derivatives.
A strong regulatory change management process helps navigate this shifting environment. By monitoring CFTC rule proposals, enforcement actions, and public statements, fintech companies can anticipate where oversight is heading. This preparation reduces the likelihood of being caught off guard and allows firms to adjust product structures and compliance programs in advance.
OCC, Federal Reserve: Bank Partnership Oversight
Many fintechs depend on partnerships with banks to deliver products. These relationships bring oversight from the OCC and the Federal Reserve, since both agencies regulate banks and set expectations for third-party risk management.
For fintech companies, this often means aligning with the compliance standards of their partner banks. Even if a rule does not apply directly to the fintech, the bank may require it as part of its own regulatory obligations. Common areas include customer due diligence, data security, vendor management, and operational controls.
The challenge is that partner banks can differ in how they apply these expectations. One bank may require extensive documentation and ongoing reporting, while another may take a lighter approach. Fintechs need flexibility to meet varied standards without creating unnecessary duplication of work.
Regulatory change management plays an important role here. By documenting how requirements are received, assessed, and implemented, fintechs can show their bank partners a clear process. This transparency helps strengthen relationships, reduces negotiation friction, and demonstrates reliability as a long-term partner.
FinCEN: AML And Transaction Monitoring
FinCEN is the primary regulator for anti-money laundering (AML) and counter-terrorist financing obligations. For fintechs, this typically means registering as a money services business when applicable, implementing customer due diligence programs, and maintaining systems for monitoring and reporting suspicious activity.
FinCEN requirements reach into many parts of fintech operations. They cover identity checks at onboarding, rules for monitoring transactions, and reporting suspicious activity. The agency also issues advisories that spotlight new risks, such as ransomware payments or fresh methods of fraud, and companies are expected to fold these into their compliance programs.
The real challenge is keeping AML frameworks effective while the business grows. Rapid customer adoption, cross-border payments, and new product features can stretch monitoring systems to their limits. If those systems aren’t updated, gaps can open that regulators or bank partners are quick to notice.
Regulatory change management provides a way to keep AML programs in step with FinCEN guidance. By reviewing updates regularly, assigning clear ownership, and tracking how changes are put into practice, fintechs can strengthen their AML systems while keeping business operations running smoothly.
State Licensing Agencies: MTLs, Lending, And Privacy Laws
State-level regulation adds one of the heaviest burdens for fintechs. Each state has its own rules for money transmission, lending, and sometimes data privacy. A company operating nationwide may need to secure dozens of licenses, each with unique application processes, renewal schedules, and reporting obligations.
The complexity grows because state rules change frequently. Some states expand their oversight of digital assets, others adjust lending limits, and many are introducing new privacy protections. Without a structured approach, it is easy for deadlines or requirements to be missed.
Fintechs that succeed here typically build a compliance calendar, assign ownership for each license, and create templates for recurring filings. Regulatory change management tools can also add value by centralizing state requirements. This turns a fragmented patchwork of state rules into a manageable workflow.
—
For fintechs, regulatory change management is a continuous process that touches every part of the business. Breaking it into clear steps makes it easier to handle and less disruptive to growth. As the rules evolve, having a structured approach helps companies stay adaptable and trusted by partners, investors, and customers.
Regly supports this work by centralizing updates, assigning tasks, and keeping clear records. It gives fintech teams a simpler way to manage change and stay focused on building their business.
Ready to Get Started?
Schedule a demo today and find out how Regly can help your business.